Innovation in occupational therapy is rapidly transforming how therapists assess, treat, and empower their clients. By integrating cutting-edge technology, occupational therapists are enhancing their ability to help individuals regain independence and improve their quality of life. From assistive technology and virtual reality to telehealth and advanced wearable devices, technology in occupational therapy is allowing for more personalized, accessible, and effective treatment options. These advancements are not only redefining traditional therapeutic approaches but are also opening doors to new possibilities in client care.
The Role of Assistive Technology in Occupational Therapy
One of the most significant innovations in occupational therapy is the development and application of assistive technology. Assistive technology encompasses devices and software that help individuals with disabilities perform tasks they would otherwise find challenging or impossible. Occupational therapists use a wide range of assistive technologies to help clients with varying needs achieve independence in their daily lives.
Types of assistive technology in occupational therapy include:
- Mobility Aids: These devices, such as manual wheelchairs, power wheelchairs, walkers, and specialized crutches, help individuals move around more freely and safely.
- Communication Devices: Speech-generating devices, adaptive keyboards, and eye-tracking software enable those with communication impairments to express themselves and communicate with others effectively.
- Adaptive Tools for Daily Living: Tools such as one-handed kitchen utensils, dressing aids, accessible mobile devices, and equipment that help with eating or grooming can make daily routines more manageable for those with limited mobility or strength.
- Electronic Aids to Daily Living: Smart home technology, like voice-activated systems or remote-controlled lighting, helps individuals with mobility and motor impairments control their environment with ease.
Occupational therapists must often tailor solutions to each client’s unique challenges, enabling them to engage in meaningful occupations with greater independence.
Wearable Devices and Occupational Therapy
Wearable devices are a form of technology in occupational therapy that has become instrumental in tracking and supporting clients’ progress. From fitness trackers to advanced rehabilitation tools, wearable devices provide real-time data that therapists can use to monitor movement patterns, activity levels, and even recovery rates. This data enables occupational therapists to adjust treatment plans based on objective metrics, leading to more precise and personalized care.
Examples of wearable devices in occupational therapy:
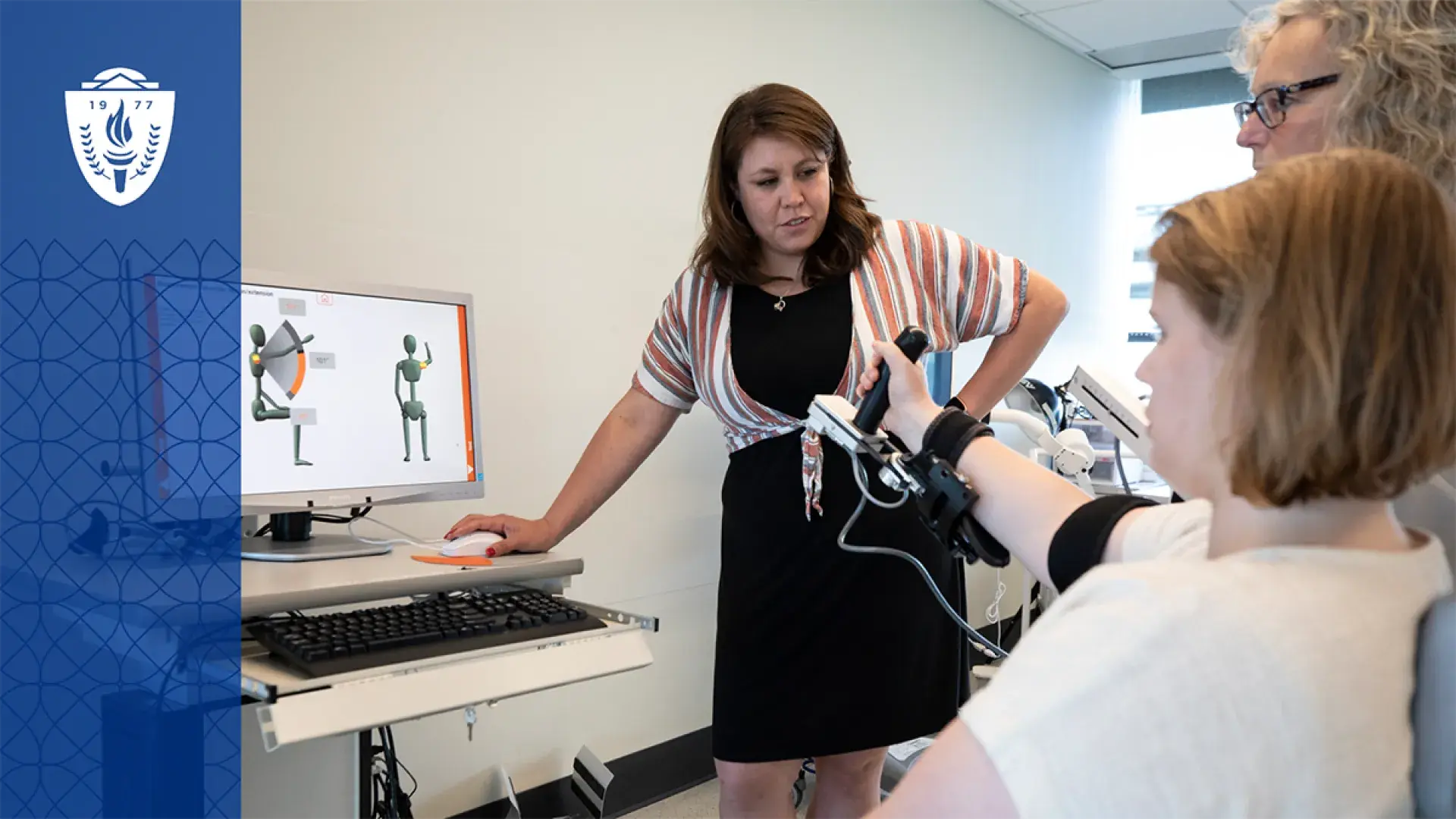
- Exoskeletons: These wearable robotic suits can help individuals with mobility impairments regain movement in their limbs. Exoskeletons provide support and strength, enabling clients to walk, lift, and perform activities they otherwise could not.
- Smart Gloves: Used to help clients with fine motor skill impairments, smart gloves provide real-time feedback on hand movements. This technology is particularly useful for clients recovering from strokes or those with neurological disorders.
- Motion Sensors and Trackers: Wearable motion sensors track joint angles, steps, and other movements, allowing therapists to monitor a client’s adherence to prescribed exercises. This technology can be used in home rehabilitation to ensure patients are performing exercises correctly, and in partnership with a client for implementing lifestyle redesign and other health-related interventions.
- Medical devices for chronic conditions: Occupational therapists support clients in using and incorporating medical devices, such as ventricular assist devices (VAD) and smart insulin pumps, into daily routines. These devices can improve management of chronic conditions and improve participation in every day activities.
Wearables have also made it easier for occupational therapists to support client engagement remotely, especially in rural or underserved areas, where in-person visits may not be feasible.
Virtual Reality in Occupational Therapy
Virtual reality (VR) is an exciting innovation in occupational therapy that enables immersive, simulated experiences for clients. VR allows occupational therapists to create customizable environments for clients to practice tasks in a safe, controlled setting. This technology can be particularly helpful for clients who need to improve cognitive skills, motor functions, or practice specific activities of daily living.
Ways VR is used in occupational therapy:
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: VR can be used to create simulations that challenge a client’s memory, problem-solving, and planning abilities, providing a safe space for practicing cognitive skills.
- Pain Management: VR has shown promise in reducing chronic pain by providing sensory distractions or immersive therapy environments, helping clients focus away from pain and engage in rehabilitative activities.
- Motor Skills Training: Clients recovering from injuries can use VR to perform exercises that improve their coordination, balance, and strength. In a virtual environment, they can practice movements without fear of injury, giving them confidence as they regain physical abilities.
The future may provide opportunities to use augmented reality as a cognitive aid. VR’s potential in occupational therapy is vast, and its interactive, engaging nature makes it a highly motivating tool for clients, enhancing the effectiveness of therapy.
Telehealth and Remote Therapy
The rise of telehealth has made a significant impact on occupational therapy, allowing therapists to reach clients remotely. Telehealth, or virtual therapy, uses video conferencing and online platforms to provide therapy sessions without requiring clients to visit a clinic. This approach increases accessibility to therapy, especially for individuals who may have limited mobility, live in remote areas, or are immunocompromised.
With telehealth becoming more widely accepted, occupational therapists can provide care to a broader client base, improving outcomes by ensuring that individuals receive the help they need regardless of their location.
Artificial Intelligence for Occupational Therapy Assessment and Planning
Software tools have become essential for occupational therapists to conduct assessments, document progress, and plan interventions. Advanced OT software includes electronic health record (EHR) systems, data analysis platforms, and scheduling tools that enhance the efficiency and accuracy of therapy services. By leveraging digital tools that are infused with artificial intelligence, occupational therapists can focus more on hands-on treatment while ensuring they are meeting regulatory standards and accurately tracking client outcomes.
Embracing the Innovation
Innovation in occupational therapy has transformed traditional practices and can open up new possibilities for treatment. From assistive technology and wearables to VR and telehealth, technology in occupational therapy is enhancing therapists’ ability to provide personalized, effective care for diverse client needs.
Training Future Occupational Therapists in Technology
The increasing role of technology in occupational therapy underscores the need for specialized training for future OTs. Programs like those offered by MGH Institute of Health Professions, the only degree-granting affiliate of Mass General Brigham, are preparing students for a future that integrates healthcare technology with clinical practice. As a leader in health professions education, MGH Institute emphasizes both interprofessional collaboration and technological competency, equipping students to utilize the latest innovations in occupational therapy and make a lasting impact in their clients’ lives.